Table of Contents
- Introduction
- SOC 2 Framework Overview
- Scoping & Preparing for SOC 2
- SOC 2 Audit Process
- Core Trust Services in Detail
- Best Practices & Compliance Tips
- SOC 2 Certification
- Value of SOC 2 Certification
- Resources & Tools
- Conclusion
Introduction
SOC 2, which stands for “Service Organization Control 2,” is a set of auditing and certification standards designed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA). It focuses on the security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of customer data held by service organizations. In essence, SOC 2 provides a framework for assessing and ensuring the trustworthiness of service providers when it comes to handling sensitive information.
Here are some key points to consider regarding SOC 2:
- Why is a SOC 2 Report Important? – SOC 2 is important because it helps organizations demonstrate their commitment to data security and privacy. In today’s digital age, businesses often rely on third-party service providers to handle critical data and perform various functions, such as cloud hosting, data processing, and software as a service (SaaS). SOC 2 compliance provides assurance to customers, partners, and stakeholders that these service providers have established effective controls to protect their data and maintain the highest standards of security.
- Who Needs SOC 2 Compliance? – Any organization that provides services that involve the processing, storage, or transmission of customer data should consider SOC 2 compliance. This includes cloud service providers, data centers, SaaS companies, IT managed service providers, and other service organizations that handle sensitive information on behalf of their clients. Additionally, companies that want to demonstrate their commitment to data security and privacy to gain a competitive edge may also pursue SOC 2 compliance.
- Benefits of SOC 2 Compliance – Achieving SOC 2 compliance offers several benefits:
- Enhanced Trust – SOC 2 compliance demonstrates to customers and partners that your organization takes data security and privacy seriously, which can build trust and confidence in your services.
- Competitive Advantage – Having SOC 2 compliance can give you a competitive edge in the market, as it sets you apart as a reliable and secure service provider.
- Risk Mitigation – By implementing robust security controls and policies, SOC 2 compliance helps reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents, potentially saving your organization from costly legal and reputational consequences.
- Operational Efficiency – The process of achieving SOC 2 compliance often leads to improved internal processes and a better understanding of data security, which can enhance overall operational efficiency.
- Attracting Customers – Many organizations, especially in highly regulated industries such as healthcare and finance, require their service providers to be SOC 2 compliant. Achieving compliance can open doors to new customers and partnerships.
In summary, SOC 2 is a critical framework for assessing and ensuring the security and privacy of customer data held by service organizations. It is important for organizations that handle sensitive data to consider SOC 2 compliance to build trust, gain a competitive advantage, and mitigate security risks.
SOC 2 Framework Overview
The SOC 2 framework is a set of auditing standards designed to assess the security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of customer data by service organizations. It is governed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) and is based on the Trust Services Criteria (TSC). Here’s an overview of the key components of SOC 2:
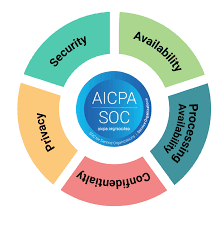
Core Trust Services Criteria (TSC)
SOC 2 is built upon five core Trust Services Criteria (TSC), which serve as the foundation for evaluating a service organization’s controls and processes:
- Security – This criterion focuses on the protection of information and systems against unauthorized access, disclosure, and damage. It assesses the effectiveness of security measures such as access controls, encryption, and incident response.
- Availability – Availability pertains to ensuring that systems and services are available for operation and use as agreed upon with customers. It evaluates aspects like system uptime, redundancy, and disaster recovery planning.
- Processing Integrity – This criterion assesses whether data processing is accurate, timely, and complete. It examines controls related to data validation, error handling, and processing accuracy.
- Confidentiality – Confidentiality addresses the protection of sensitive information from unauthorized access or disclosure. It evaluates controls like data classification, encryption, and data access restrictions.
- Privacy – Privacy criteria assess how well an organization manages and protects personal information in accordance with its privacy policy and relevant regulations.
Source: Certn
Differences between SOC 2 and Other Compliance Standards
- SOC 2 vs. SOC 1 – SOC 2 is designed for service organizations that handle customer data, whereas SOC 1 (System and Organization Controls 1) is intended for organizations that provide services impacting the financial reporting of their clients. SOC 1 focuses on internal controls related to financial reporting, while SOC 2 is broader and covers security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
- SOC 2 vs. ISO 27001 – While both SOC 2 and ISO 27001 address information security, they have different scopes and purposes. SOC 2 is specifically designed for service organizations to assess controls related to customer data protection. ISO 27001, on the other hand, is a globally recognized information security management system (ISMS) standard that can be applied to any organization. ISO 27001 covers a wider range of security controls and is not limited to service providers. Additionally, ISO 27001 requires a risk management approach, while SOC 2 is more focused on control objectives and criteria.
In summary, SOC 2 is a framework that evaluates service organizations’ controls and processes related to security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of customer data. It differs from other compliance standards like SOC 1 and ISO 27001 in terms of scope and focus, making it particularly relevant for service providers handling sensitive customer information.
Scoping and Preparing for SOC 2
Preparing for a SOC 2 assessment involves several important steps, including defining the scope of the assessment, selecting applicable Trust Services Criteria (TSC) criteria, assembling a project team, conducting a risk assessment and gap analysis, and setting clear goals and objectives. Here’s an overview of each of these steps:
- Defining the Scope of Assessment – Start by clearly defining the scope of your SOC 2 assessment. Determine which systems, processes, and services will be included in the assessment. The scope should consider the specific services that impact the security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of customer data. It’s important to document the boundaries of what is included and excluded from the assessment to avoid scope creep.
- Selecting Applicable TSC Criteria – Review the five Trust Services Criteria (TSC) categories: Security, Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, and Privacy. Based on your organization’s services and the nature of the data you handle, select the relevant TSC criteria that will apply to your assessment. Not all criteria may be applicable to your organization, so focus on those that align with your business operations.
- Building a Project Team – Assemble a dedicated project team responsible for overseeing the SOC 2 compliance initiative. This team should include individuals with expertise in information security, compliance, and relevant operational areas. Key roles may include a project manager, IT security professionals, legal counsel, and representatives from business units that handle customer data.
- Risk Assessment and Gap Analysis – Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment and gap analysis to identify potential security and compliance vulnerabilities within your organization. This process involves evaluating your current controls and practices against the selected TSC criteria. Identify weaknesses, risks, and areas where controls need improvement or implementation. This step is crucial for understanding the gaps that must be addressed to achieve SOC 2 compliance.
- Setting Goals and Objectives – Define clear and measurable goals and objectives for your SOC 2 compliance initiative. These goals should align with the selected TSC criteria and address the gaps identified during the risk assessment. Goals could include improving access control procedures, enhancing data encryption practices, or establishing an incident response plan. Establish realistic timelines for achieving these objectives and allocate resources accordingly.
Once you’ve completed these steps, you’ll be in a better position to initiate the SOC 2 compliance process. It’s important to note that achieving SOC 2 compliance is an ongoing effort that requires continuous monitoring and improvement of controls and practices to ensure the security and privacy of customer data. Regular assessments and audits are necessary to maintain compliance and demonstrate your commitment to data protection to customers and stakeholders.
SOC 2 Audit Process
The SOC 2 audit process involves several key steps, from selecting a qualified CPA (Certified Public Accountant) firm to reporting and communication of audit findings. Here’s an overview of each of these steps:
- Selection of a Qualified CPA Firm – Choose a reputable and qualified CPA firm that specializes in SOC 2 audits. The CPA firm will be responsible for conducting the assessment and issuing the final SOC 2 report. Consider factors such as the firm’s experience, expertise, and industry reputation when making your selection.
- Planning the Audit – Work closely with the chosen CPA firm to plan the audit. This includes defining the scope of the audit, specifying the selected Trust Services Criteria (TSC) criteria, and establishing the audit objectives. The planning phase also involves coordinating schedules and logistics for the audit process.
- Onsite vs. Remote Audit Considerations – Decide whether the audit will be conducted onsite, where auditors physically visit your facilities, or remotely. The choice may depend on factors like the nature of your services, the geographic location of your organization, and the availability of remote audit tools and technologies. Remote audits have become more common, especially in light of global events like the COVID-19 pandemic, but the decision should align with the audit objectives and security considerations.
- Audit Timeline and Milestones – Establish a clear timeline for the audit process, including key milestones and deadlines. This timeline should account for the planning phase, data gathering, audit testing, and reporting. Ensure that all parties involved are aware of the schedule to facilitate a smooth audit process.
- Collecting Evidence and Documentation – During the audit, the CPA firm will request evidence and documentation to verify the effectiveness of your controls and processes related to the selected TSC criteria. This evidence may include policies, procedures, access logs, incident response plans, and other relevant documentation. It’s important to organize and provide this information promptly to minimize delays in the audit process.
- Audit Testing and Procedures – The auditors will perform testing and procedures to assess the controls in place. This may involve interviewing employees, reviewing documentation, and conducting technical assessments. The goal is to evaluate whether your organization’s controls align with the TSC criteria and effectively protect customer data.
- Reporting and Communication – After completing the audit, the CPA firm will issue an SOC 2 report. This report typically includes a description of the scope of the audit, an opinion on the effectiveness of controls, and details on any identified control deficiencies or exceptions. The report may come in two main forms: a SOC 2 Type I report, which assesses the design of controls at a specific point in time, and a SOC 2 Type II report, which evaluates the operating effectiveness of controls over a specified period (usually six to twelve months). Share the report with relevant stakeholders, such as customers, partners, and management.
Throughout the audit process, effective communication and cooperation between your organization and the CPA firm are critical to its success. Address any identified control deficiencies promptly and work with the auditors to ensure compliance with the selected TSC criteria. The SOC 2 report provides valuable assurance to customers and stakeholders regarding your organization’s commitment to data security and privacy.
Core Trust Services Criteria in Detail
The Core Trust Services Criteria (TSC) are an essential part of the SOC 2 framework, and they provide a framework for evaluating the security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy of customer data held by service organizations. Let’s delve into the details of each TSC category:
Security
- Access Controls – Access controls involve policies and procedures to restrict access to systems and data only to authorized individuals. This includes user authentication, authorization, and the principle of least privilege.
- Encryption– focuses on protecting data at rest and in transit through encryption mechanisms. It ensures that sensitive information remains confidential even if unauthorized access occurs.
- Incident Response -Incident response outlines how an organization responds to security incidents, such as data breaches or cyberattacks. It includes procedures for detecting, reporting, and mitigating incidents.
- Risk Management – Risk management involves identifying and assessing potential security risks and implementing measures to mitigate them. This includes risk assessment, risk analysis, and the development of risk mitigation strategies.
Availability
- System Uptime – Availability pertains to ensuring that systems and services are available for operation and use as agreed upon with customers. This includes monitoring system uptime, downtime, and service-level agreements (SLAs).
- Redundancy and Failover – Redundancy and failover measures ensure that critical systems and data are redundantly backed up and can fail over to alternative systems in the event of a failure. This helps maintain service continuity.
Processing Integrity
- Data Accuracy – Processing integrity verifies that data processing is accurate, complete, and timely. It ensures that data is not subject to unauthorized alteration or manipulation.
- System Processing – System processing controls evaluate the integrity and reliability of system processes, data validation, and error-handling mechanisms.
Confidentiality
- Data Classification – Data classification involves categorizing data based on its sensitivity and importance. It helps organizations apply appropriate access controls and protection measures to different types of data.
- Information Access – Information access controls ensure that only authorized individuals have access to confidential data. This includes user authentication, authorization, and monitoring of data access.
Privacy
- Personal Data Protection – Privacy criteria assess how well an organization manages and protects personal information. This includes policies and practices related to data collection, processing, and storage.
- GDPR and SOC 2 Intersection – The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a European data privacy regulation. SOC 2 and GDPR have some overlap, particularly regarding data protection and privacy. Organizations that handle the personal data of EU residents may need to consider both SOC 2 and GDPR requirements to ensure compliance.

Source: Akitra
It’s important to note that for a SOC 2 assessment, an organization selects which of these TSC criteria are applicable based on their services and the nature of the data they handle. The criteria chosen will guide the assessment process and help demonstrate the organization’s commitment to safeguarding customer data and maintaining high standards of security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
Best Practices and Compliance Tips
Implementing best practices and compliance tips is crucial for achieving and maintaining SOC 2 compliance. Here are some recommendations for each of the mentioned areas:
Implementing Security Policies and Procedures
- Develop comprehensive security policies and procedures that align with the Trust Services Criteria (TSC) relevant to your organization.
- Ensure that policies cover areas such as access controls, data encryption, incident response, and risk management.
- Regularly review and update policies to reflect changes in technology, threats, and regulatory requirements.
Monitoring and Alerting
- Implement a robust monitoring and alerting system to continuously track security events and potential threats.
- Set up alerts for suspicious activities, unauthorized access attempts, and system vulnerabilities.
- Establish incident response procedures to address security incidents promptly.
Continuous Improvement
- Embrace a culture of continuous improvement by regularly assessing and enhancing your security controls and processes.
- Conduct regular security assessments, vulnerability scans, and penetration tests to identify weaknesses.
- Learn from security incidents and near misses to strengthen your security posture.
Third-Party Vendor Management
- If you rely on third-party vendors for services, ensure they meet your security and compliance standards.
- Conduct due diligence when selecting vendors and reviewing their SOC 2 reports or other compliance documentation.
- Establish clear expectations and contractual obligations related to security and data protection.
Documentation and Record-Keeping
- Maintain thorough documentation of security policies, procedures, and controls.
- Document all security incidents, including their resolution and lessons learned.
- Keep records of employee training and awareness programs to demonstrate compliance efforts.
Employee Training and Awareness
- Train employees on security best practices, data protection, and their roles in safeguarding customer data.
- Conduct regular security awareness programs to keep employees informed about emerging threats and the importance of security.
- Encourage employees to report security concerns or incidents promptly.
Access Controls and Least Privilege
- Enforce strong access controls, including multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strong password policies.
- Follow the principle of least privilege, ensuring that employees have access only to the data and systems necessary for their roles.
- Regularly review and update user access permissions to align with changes in job roles and responsibilities.
Data Encryption
- Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit using strong encryption algorithms.
- Implement encryption for databases, files, emails, and any other data storage or transmission mechanisms.
- Periodically review and update encryption practices to stay aligned with industry standards.
SOC 2 Certification
SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2) certification is a set of standards for managing customer data based on five trust service criteria: security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. SOC 2 reports are typically issued by third-party auditors to evaluate and verify an organization’s adherence to these criteria. There are two main types of SOC 2 reports: Type 1 and Type 2.
SOC 2 Type 1 Report
- A SOC 2 Type 1 report is a snapshot assessment of an organization’s controls and processes at a specific point in time. It provides an auditor’s opinion on the design and implementation of controls related to the trust service criteria as of a specific date.
- It is mainly concerned with evaluating whether the organization’s control systems are suitably designed to meet the criteria and whether they have been implemented as of the assessment date.
- It does not provide assurance about the ongoing effectiveness of these controls but rather focuses on their existence and design at the time of the audit.
SOC 2 Type 2 Report
- A SOC 2 Type 2 report provides a more comprehensive assessment than Type 1. It includes all the elements of a Type 1 report, but in addition, it evaluates the effectiveness of those controls over a specified period, typically a minimum of six months.
- Type 2 reports are concerned not only with the design of controls but also with their operational effectiveness. Auditors assess whether the controls were consistently in place and functioning effectively throughout the specified period.
- Type 2 reports are generally considered more valuable because they provide insight into an organization’s ability to maintain and operate controls over time.
The Value of SOC 2 Certification
SOC 2 certification is valuable for service organizations, particularly those that handle sensitive customer data, for several reasons:
- Trust and Assurance: SOC 2 certification provides assurance to customers and stakeholders that an organization has implemented and maintained effective controls to protect their data.
- Competitive Advantage: Having a SOC 2 certification can be a competitive advantage in the marketplace, as it demonstrates a commitment to security and compliance.
- Regulatory Compliance: SOC 2 certification can help organizations meet various regulatory requirements, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or other industry-specific standards.
- Risk Mitigation: By identifying and addressing security and compliance risks, organizations can reduce the likelihood of data breaches and associated financial and reputational damages.
Maintaining SOC 2 Compliance
Maintaining compliance is an ongoing process that involves the following steps:
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits, especially if you have a Type 2 report, to ensure that controls remain effective and are consistently implemented.
- Monitoring: Continuously monitor systems and processes for security and compliance issues.
- Updates and Improvements: Keep controls and security measures up to date to address evolving threats and vulnerabilities.
- Documentation: Maintain thorough documentation of policies, procedures, and control activities.
- Training and Awareness: Ensure that employees are trained and aware of their responsibilities regarding security and compliance.
- Incident Response: Develop and maintain an incident response plan to address security incidents promptly.
- Third-Party Risk Management: Evaluate and monitor the security practices of third-party vendors and partners that have access to your systems or data.
By following these steps and regularly assessing and improving your controls, you can maintain SOC 2 compliance over time and demonstrate your commitment to safeguarding customer data.
Common Challenges
- Scope Definition: Defining the scope of a SOC 2 audit and determining which systems and processes are in scope can be challenging. It’s important to accurately identify the systems and services that handle customer data and are subject to the audit.
- Control Design and Implementation: Ensuring that controls are not only designed appropriately but also consistently implemented and followed by employees can be a challenge. Inadequate control design or inconsistent implementation can lead to compliance issues.
- Change Management: Keeping up with changes in your organization’s processes, systems, and infrastructure can be challenging. Changes may impact the effectiveness of existing controls and need to be managed carefully.
- Lack of Documentation: Inadequate documentation of policies, procedures, and control activities is a common pitfall. Auditors rely on documentation to assess compliance, so it’s crucial to maintain thorough records.
- Third-Party Risk: Assessing and managing the security practices of third-party vendors and partners can be complex. Failure to address third-party risks can lead to compliance issues, especially if those third parties have access to customer data.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Ensuring that all employees are trained and aware of their responsibilities regarding security and compliance is essential. Lack of awareness and training can result in non-compliance.
- Incident Response: Inadequate incident response plans and procedures can be a significant challenge. Organizations need to have a well-defined plan in place to handle security incidents promptly and effectively.
Resources and Tools
Here are some resources, templates, recommended software/tools, and additional reading/references that can help you with SOC 2 compliance:
SOC 2 Compliance Checklist
- AICPA SOC 2 Guide: The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) provides a comprehensive guide that includes a SOC 2 compliance checklist. This guide can help you understand the requirements and prepare for your audit.
Templates and Sample Documentation
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) offers various templates and resources for cybersecurity and compliance, which can be valuable for SOC 2 compliance documentation.
- AICPA SOC 2 Templates: The AICPA provides sample templates for various SOC 2 documentation, including policies, procedures, and control narratives. These templates can serve as a useful starting point.
- ISO 27001 Documentation Toolkit: Although ISO 27001 is a different standard, its documentation toolkit can provide templates and examples of security policies and procedures that may be relevant to SOC 2 compliance.

Recommended Software and Tools
- GRC (Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance) Software: There are several GRC software solutions available that can help with SOC 2 compliance management, including tools for policy management, risk assessment, and audit management. Some popular options include:
- RSA Archer
- ServiceNow GRC
- MetricStream
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Tools: SIEM tools like Splunk, IBM QRadar, and LogRhythm can assist with real-time monitoring and alerting, which is important for meeting SOC 2 requirements related to security incidents.
- Vulnerability Management Tools: Tools like Qualys, Nessus, and Tenable can help you scan and assess your infrastructure for vulnerabilities, which is crucial for maintaining SOC 2 compliance.
- Document Management Software: Tools like Microsoft SharePoint, Google Workspace, or specialized document management software can help you organize and maintain the documentation required for SOC 2 compliance.
Additional Reading and References
- SOC 2 Trust Services Criteria: Familiarize yourself with the five trust service criteria (security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy) outlined by the AICPA.
- AICPA SOC 2 Reporting Guide: The AICPA offers a comprehensive SOC 2 reporting guide that provides detailed information on the standard, the audit process, and reporting requirements.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: Consider reading NIST’s Cybersecurity Framework, as it provides valuable guidance on improving and assessing cybersecurity practices, which aligns with SOC 2 compliance.
- ISACA: The Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA) is a valuable resource for cybersecurity and compliance professionals. Their publications and resources can provide additional insights into best practices.
- Online Forums and Communities: Participating in online forums and communities like ISACA’s, Reddit’s /r/cybersecurity, and LinkedIn groups focused on compliance and security can be a great way to learn from others’ experiences and ask questions.
Remember that SOC 2 compliance can be complex, and it’s often beneficial to work with experienced auditors and consultants to ensure that you meet the requirements effectively. Additionally, staying up to date with industry trends and best practices is crucial for maintaining compliance in a rapidly evolving cybersecurity landscape.
Conclusion
SOC 2 compliance is important in today’s digital age, where data security and trust are paramount. Organizations that commit to SOC 2 compliance demonstrate their dedication to protecting customer data and maintaining the highest standards of security and privacy. Here are key points to consider:
The Significance of SOC 2 Compliance
- SOC 2 compliance is not just a checkbox on a list of requirements; it represents a commitment to safeguarding sensitive customer data.
- It provides assurance to customers, partners, and stakeholders that an organization has implemented and maintained robust controls to protect their data.
- Compliance with SOC 2 can be a competitive advantage, as it can set an organization apart in terms of security and trustworthiness in the marketplace.
The Ongoing Commitment to Data Security and Trust
- SOC 2 compliance is not a one-time effort: it’s an ongoing commitment to data security and trust.
- Maintaining compliance requires continuous monitoring, regular audits, and a dedication to improving security practices.
- It involves adapting to evolving threats and vulnerabilities and staying up to date with industry best practices.
Encouragement for Organizations to Embark on SOC 2 Compliance Journeys
- While SOC 2 compliance can be challenging, it’s a worthwhile journey for organizations that handle sensitive data.
- It helps organizations identify and mitigate risks, prevent data breaches, and build trust with customers and partners.
- The lessons learned from SOC 2 audits and the improvements made in security and compliance processes can benefit an organization beyond just meeting the requirements.
In an era where data breaches and cybersecurity incidents are all too common, SOC 2 compliance serves as a beacon of trust. It not only protects an organization from potential financial and reputational damage but also fosters stronger customer relationships and establishes credibility in an increasingly data-driven world. Organizations that embrace SOC 2 compliance are not only safeguarding their data but also demonstrating their commitment to the security and privacy of those they serve.